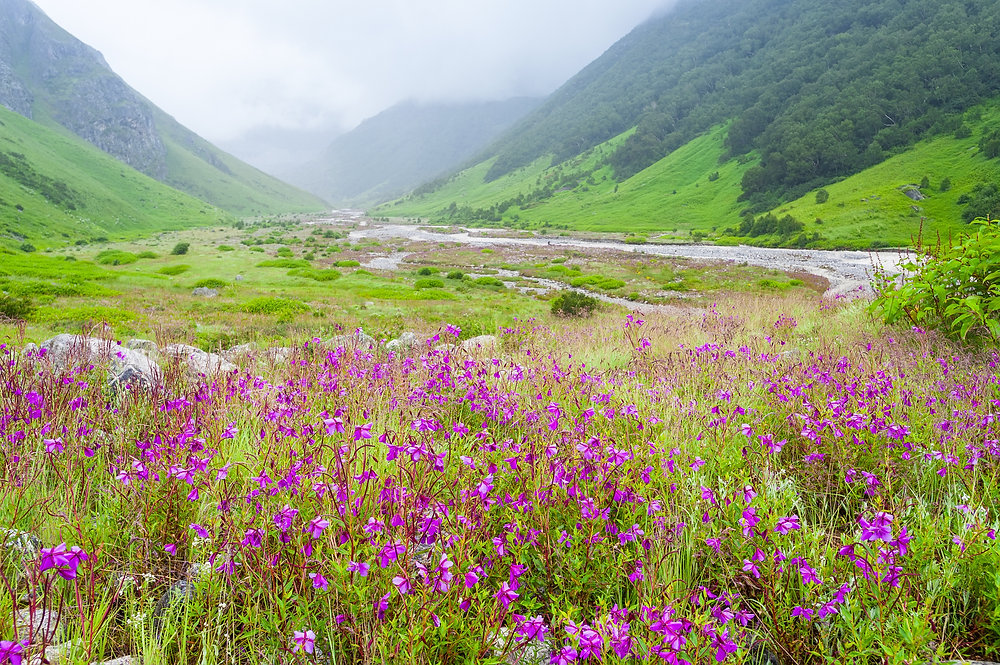
Uttarakhand has taken a strong step toward environmental protection by launching a Plant Conservation Mission focused on preserving rare and endangered plant species found in the Himalayan region. This effort highlights the state’s commitment to protecting its unique biodiversity and promoting ecological sustainability.
Why Uttarakhand Launched This Initiative Plant Conservation Mission
The rich biodiversity of Uttarakhand is under constant threat due to climate change, deforestation, and human activities. The Plant Conservation Mission was launched to prevent the extinction of several endangered plant species and to ensure their survival for future generations. Many of these plants have medicinal and cultural value, making their conservation even more critical.
Focus on Endangered and Rare Plant Species
This mission aims to conserve over 1,000 rare and endangered plants, including Himalayan rare herbs like Atis, Kutki, and Brahma Kamal. These species are vital to traditional medicine and are disappearing rapidly from their natural habitats. By identifying, mapping, and securing these plants, the mission hopes to reverse the loss and promote growth in controlled environments.
Key Regions Targeted for Restoration
The program will focus on the Alaknanda, Bhagirathi, and Tons valleys, where many rare plants grow naturally. These high-altitude regions are ideal for restoring plant populations because of their unique climate and soil conditions. The government will also set up plant conservation zones in forest areas and biodiversity parks to protect and propagate these species.
Role of Scientists and Local Communities
Botanists, researchers, and forest officials are playing a key role in identifying threatened species and planning their protection. However, the active involvement of local communities is equally important. People living in the region are being trained to help in seed collection, planting, and monitoring plant growth. Their traditional knowledge about Himalayan herbs adds great value to the project.
Medicinal and Ecological Benefits Expected
Many of the plants being preserved have high medicinal value and are used in Ayurveda. For example, Kutki is known for liver health, while Atis is used to treat fever and digestive issues. Besides health benefits, these plants help maintain ecological balance by supporting the food chain and enhancing soil quality.
Source: GKToday – Uttarakhand Launches Endangered Plant Conservation Program
Long-Term Vision for Plant Conservation
The Plant Conservation Mission is not just a short-term project. Uttarakhand plans to make this a long-term initiative by integrating plant conservation with environmental education, eco-tourism, and sustainable agriculture. The goal is to create a self-sustaining model that balances conservation with development and empowers communities to protect their natural heritage.
This mission marks a major step toward saving India’s rare plants and promoting sustainable environmental practices. As the plant conservation program moves forward, it may inspire similar efforts across other Himalayan states.
Stay tuned with Notifire for more updates.